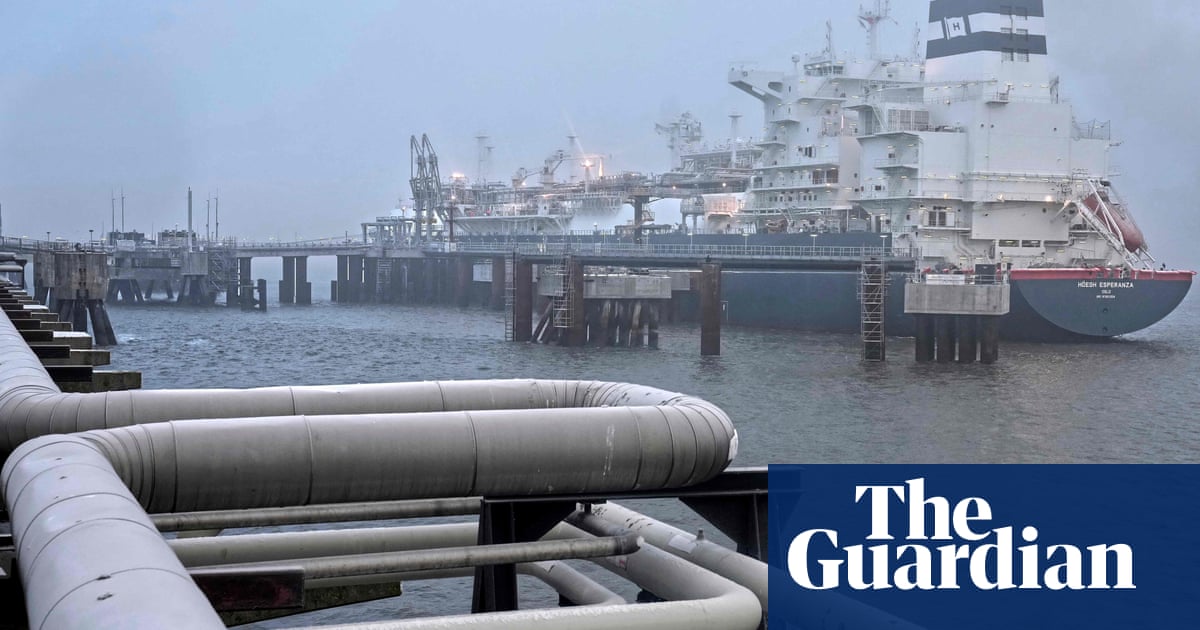
Europe purchased a file quantity of liquefied pure fuel from Russia final 12 months, knowledge reveals, regardless of EU efforts to ditch the fossil fuels funding Putin’s struggle chest.
Ships carrying 17.8m tonnes of ultra-cold Russian fuel docked in European ports in 2024, up by greater than 2m tonnes from the 12 months earlier than, in response to analysts Rystad Power.
Jan-Eric Fähnrich, a fuel analyst at Rystad Power, stated LNG flows weren’t solely on the rise however “at file ranges”.
Europe has slashed its huge imports of piped Russian fuel for the reason that begin of the Ukraine struggle however has more and more bought shipments of LNG from a variety of nations, together with Russia. Final 12 months, it overtook Qatar as Europe’s second-biggest provider of LNG, behind the US.
In 2024, Europe introduced in 49.5bn cubic metres (bcm) of Russian fuel via pipelines, and an extra 24.2bcm in chilly liquid kind on ships, in response to Fähnrich. A few of the LNG can have been resold to different nations, he added.
The figures have been revealed days after Ukraine stopped flows of Russian fuel via its pipelines, ending a Soviet-era power route that had survived three years of full-scale struggle between the neighbours.
Campaigners have argued the EU is undermining its assist for Ukraine and its personal local weather objectives by persevering with to pay Russia for fuels that spew planet-heating particles when burned. Because the struggle, the EU has lower demand for power and loosened guidelines to construct wind generators and photo voltaic panels, however scientists say it’s nonetheless not cleansing its economic system as quick because it ought to to maintain the planet from heating 1.5C (2.7F) by the top of the century.
Information from the Centre for Analysis on Power and Clear Air (Crea), whose figures differ barely from Rystad’s, confirmed EU imports of Russian LNG got here to €7.32bn in 2024. It discovered a 14% year-on-year rise in quantity that introduced imports to 17.5m tonnes.
“The explanation for the rise is pretty easy,” stated Vaibhav Raghunandan, a Russia analyst at Crea. “Russian LNG is obtainable at a reduction to various suppliers … With no sanctions imposed on the commodity, firms are working in their very own self-interest and shopping for rising portions of fuel from the most cost effective provider.”
The EU goals to cease importing Russian fossil fuels by 2027 but it surely has been reluctant to sanction fuel because it has carried out for coal and oil. In June, member states agreed to ban the “transshipment” of Russian LNG that goes on to non-EU nations from March 2025. The current rise in Russian LNG imports might have been pushed up by efforts to ship volumes earlier than sanctions hit, stated Fähnrich.
Ukrainian activists argue the sanctions regime is being undermined by “obtrusive loopholes” that also let Russia fund its struggle machine with fossil gas revenues.
“The file ranges of Russian LNG imports in 2024 are a stark reminder that the EU should act decisively to shut the remaining loopholes in its sanctions regime,” stated Svitlana Romanko, founding father of Razom We Stand, a Ukrainian local weather marketing campaign group. “We’re as much as 15 sanctions packages now, and a full ban on Russian LNG imports is urgently wanted to cease funding Putin’s struggle chest.”
She additionally known as on the EU to crack down on Russia’s “shadow fleet” of previous and underinsured tankers, and to shut a refining loophole that lets Europe import merchandise created from Russian crude oil in nations akin to Turkey and India.
Tighter sanctions may lower greenhouse fuel air pollution related to Russia’s upstream oil and fuel by 25% by 2030, a report from Romanko and her colleagues discovered final month. If renewables have been to interchange the soiled fuels, end-use emissions may fall by 300m tonnes a 12 months, the report discovered.
“The EU has a alternative,” stated Romanko. “Proceed financing struggle and air pollution, or decide to a clear, safe, and peaceable power future.”
Supply hyperlink